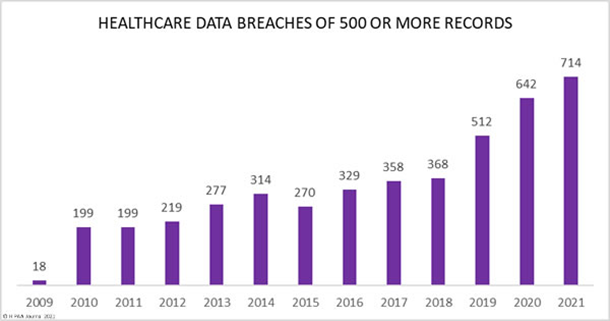
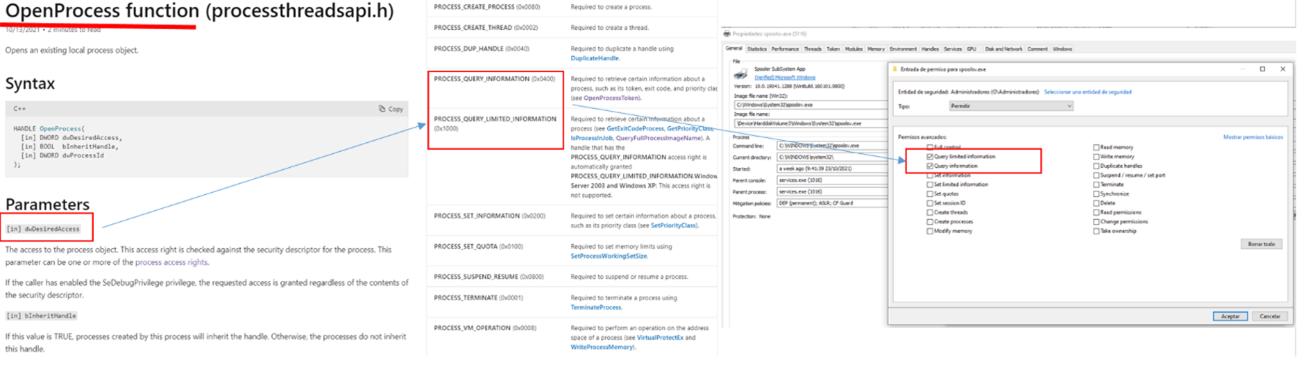
During the last quarter of 2022, the Lab52 team has conducted an in-depth analysis of the threats that have been active during the period, focusing on information from both public and private sources, as well as studying the geopolitical context in order to anticipate potential campaigns.
Below is the report for the quarter, which includes the main trends of the period, along with analysis of the most sophisticated threats and the most important geopolitical events.
The intelligence gathering and analysis carried out by the Lab52 cyberintelligence team has led to a series of conclusions and generated intelligence for S2 Grupo’s security services.