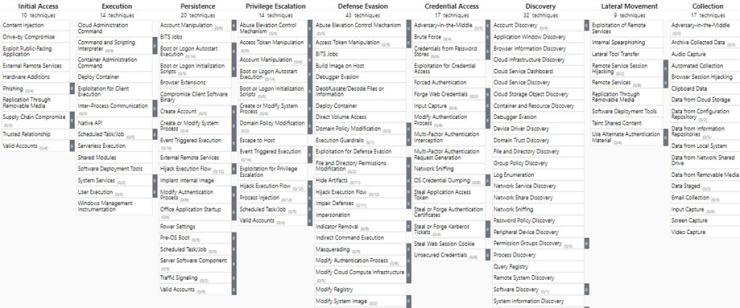
In today’s cybersecurity landscape, the complexity of the solutions implemented to protect against growing threats is constantly increasing. Because of this, both malicious actors, who seek to compromise organizations and systems for their own benefit, and Red Team operators, whose mission is to identify and report vulnerabilities for later remediation, are driven to identify and exploit new weaknesses in systems, adapting their methods and developing new TTPs that allow them to evade existing defenses.
The tools developed by both operators and hostile attackers are designed for evasion of security solutions such as EDRs. This is because keeping the operation off the Blue Team’s radar is of vital importance. Being detected would result in the defense team obtaining IOCs, which they would use to dismantle an entire operation, blocking IP addresses and domains, creating YARAs for artifacts or implementing the latest updates to all their security solutions.
These actions, in addition to increasing the Blue Team’s alert level, would mean the end or restart of an attack or operation, as the entry vector could be mitigated or directly blocked and the infrastructure would need to be almost completely reassembled. This is why maintaining the OPSEC of an operation is of vital importance, avoiding the generation of alerts that could notify the defenders and thus meet the objective without being detected.
[Read more…]